What is DVT?
What is DVT?
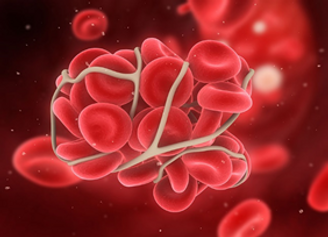
DVT stands for Deep Vein Thrombosis, in a simple language we can say that the blood clotted deep inside of the vein is known as deep vein thrombosis. These are the blood clots which form in deep veins and hence can go unnoticed.
The DVTs mostly observed in legs, thighs, and pelvis but it can also take place in arms, body, liver, kidney and brain.

What is the danger of having DVT?
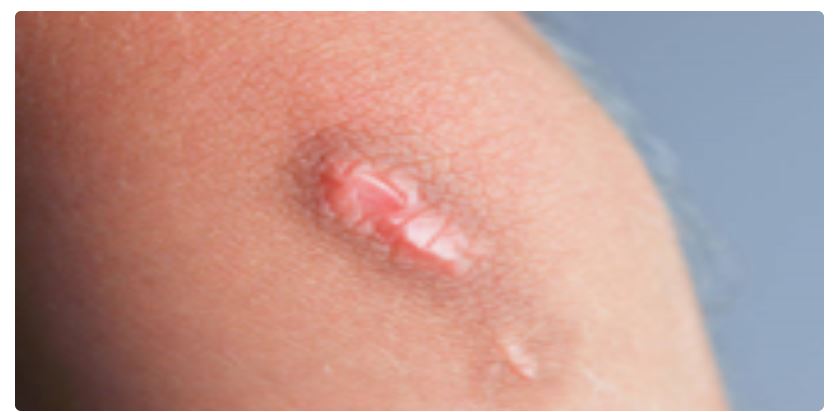
DVT blocks the blood flow in affected vein which can make the portion hot and swollen. The skin could darken and turn red or blue and might look stretched and shiny. The most worrying aspect of having a DVT is that the blood clot might break away from its original location and move through the bloodstream. If this happens, the clot could end up blocking a vein in the lung, causing a pulmonary embolism which is a potentially life-threatening complication. Because of this risk factor, DVT requires immediate medical attention.
A compelling fact here one should be mention is that 1 out of 4 people die due to the diseases related to the blood clot. And you will be shocked to know that DVT is the #1 cause for the preventable deaths in the hospitals.
What are the symptoms of DVT?
35% of the people with DVT don’t have any symptoms or the symptoms may be so minute that they would go unnoticed. The symptoms associated with DVT include:
- Swelling in your legs.
- Change in the skin colour.
- The skin may become red or purple depending upon the colour of your skin.
- The swollen area may feel warm.
- The pain in the DVT affected leg.
People usually ignore these symptoms until the clot travels to your lungs and it develops the severe condition; so it is important to consult your doctor when you observe these symptoms.
Adverse effects of DVT
1) Death
2) Recurrence
3) Pulmonary Embolism
What is Pulmonary Embolism?
If the blood clot breaks off and travels to lungs, causing a blockage, it is called “Pulmonary Embolism” or PE. It is a common and potentially lethal condition, as most of the patients who succumb to PE do so within the first few hours of the event. Nearly all PE’s arise from thrombi in the lower extremity OR pelvic veins (i.e. Deep Venous Thrombosis) The risk of embolization is higher with thrombi proximal to the calf veins.

What is Post Thrombotic Syndrome?
Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) is a venous stress disorder that develops from long-term effects from a previous deep venous thrombosis (DVT).
DVT causes rupture of small superficial veins and increases pressure in the deep veins and capillaries. This causes Pain, Swelling, varicose veins, ulcers. PTS can affect 23-60% of patients in the two years following DVT of the leg. Treatment options for PTS include proper leg elevation, compression therapy, or electrostimulation devices, pharmacotherapy (pentoxifylline), herbal remedies (such as horse chestnut, rutosides), and wound care for leg ulcers.
What are the factors that can cause Thrombosis?
- Having a history of DVT in your family.
- Having limited blood flow in a deep vein because of an injury, surgery or immobilization.
- Age factor (above 40).
- Obesity.
- Having Varicose Veins.
- Lacking the body movement.
- Taking the birth control pills.
- Smoking
Resources used: 1) Mayo clinic Website
2) Cleveland Clinic Website