Mechanical CardioPulmonary Resuscitation
What is Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA)?
In scientific terms, Sudden Cardiac Arrest is the cessation of cardiac mechanical activity as confirmed by the absence of signs of circulation of blood. Oxygen rich blood supplies to vital organs like Heart, Brain & Lungs stops which leads to morbidity & mortality.1 In simpler terms, Sudden Cardiac Arrest is a life-threatening
emergency where a person becomes unresponsive and stops breathing or only gasps. It often occurs due to a heart attack, respiratory failure or an electrical problem in the heart.
Cardiac Arrest remains a leading cause of death worldwide, with survival rates heavily dependent on timely intervention and widespread public knowledge of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). In India, an estimated 700,000 people die annually due to sudden cardiac arrest (SCA), a significant public health issue with a low survival rate, particularly for out-of-hospital cases.
Note: **Cardiac arrest doesn’t care who you are, how old you are, or where you are. SCA may happen anytime, anywhere. Most people don’t know that performing CPR within the first few minutes can double or even triple the chances of survival.**
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)-
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation is a critical emergency procedure that can save lives during cardiac arrest. It involves manually compressing the chest to circulate blood & oxygen throughout the body, helping to keep vital organs alive & functional until advanced medical care can be provided or vitals are restored. Such a situation is crucial because brain cells start to die within four minutes of cardiac arrest due to lack of oxygen. By performing CPR, you help maintain blood flow to the brain and other vital organs, which can prevent irreversible brain damage and increase the chances of survival. For every minute without CPR, the likelihood of survival decreases by approximately 10%, making quick action essential.
CPR, a quick and effective action in such a situation can make the difference between life and death. Whether at home, at work, or in public, this life-saving skill is invaluable.
**Note- SCA is a global health issue but only developed cities like USA, UK are equipped with the Emergency Medical Services and India lacks formal sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) registry and the infrastructure for a robust emergency medical services (EMS) response system.2**
Steps to perform CPR:
There are three parts of performing CPR and they can be remembered as “CAB”: C for compressions which is 100-120 per minute, A for airway-After 30 chest compression, blow mouth to mouth air and B for breathing.
When to start Performing CPR: In an untoward event of SCA:
- Check for responsiveness: Gently tap and shout to see if the person responds.
- Call for help: Immediately dial emergency services.
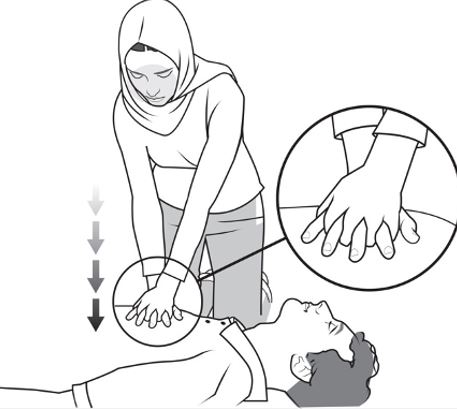
- Chest Compressions: Push hard and fast in the center of the chest (about 2 inches deep and at 100-120 compressions per minute).
- Rescue Breaths: If trained, provide rescue breaths after every 30 chest compressions.
- Continue CPR until professional help arrives or the person shows signs of life.

Providing manual CPR to a patient in cardiac arrest
Challenges of Performing CPR:
- It Requires Meticulous Training of CPR.
- 100-120 Compression per minute is the key & delivering it is physically demanding, CPR providers may run out of energy in a few minutes resulting in missing continuity & rhythm required to get optimum outcome.
- Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest (OHCA) events may pose other challenges to effective CPR i.e. Surroundings (Moving Vehicle, Public Transport, Play Ground.)
- The ability of the rescuer to perform continuous compressions effectively without being tired plays a pivotal role.
Other factors which limit the quality of CPR are Mattress type lying beneath the patient, body weight of the rescuer and hand positioning of the rescuer for adequate chest compression depth.3
To alleviate the traumatic experience and challenges involved in performing CPR when a person suffers cardiac arrest, a new device
has been innovated by Codex Healthcare Pvt. Ltd. Codex developed a Mechanical Cardio Pulmonary Device which provides high-quality chest compressions over extended periods, which can be difficult for humans to sustain. This mechanical Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) device by Codex operates on battery power, ensuring effective and efficient compressions until advanced life support is available.
Applications of the Mechanical CardioPulmonary Resuscitation Device–
This light weight and chargeable device is to provide CPR where continuous manual CPR is almost impractical, such as ambulances, helicopters, and locations where the patient is in constant motion. The device can be used in Sports Club, Hospitals, Offices, Public Places etc. It works as a blessing for the areas where the people don’t know how to perform CPR.
**Note- During the sporting activities, it is always important to have emergency aid duly available in case of cardiac emergency situations as this is a global health issue.**
3 simple steps to use Mechanical CPR
- Place a plastic support sheet below the back of the patient.
- Secure hands and place moving disc on chest.
- Switch on and assess if the disc is adequately compressing chest.
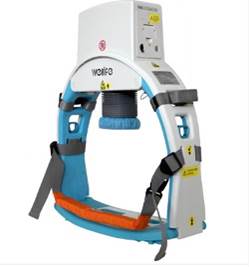
Figure 1 Codex Mechanical Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Device
Percentage of people saved with CPR:
For the past 20 years, the survival rate for cardiac arrest has hovered around 10 percent for out-of-hospital incidences and 21 percent for in- hospital events, yet research shows that high-quality CPR has a significant impact on survival outcomes, whether inside or outside the hospital.
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) is a public health burden accounting for nearly 10% of global mortality and 50% of cardiovascular deaths. Its worldwide incidence is 55 per 100,000 person-years. Providing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is the most critical step in the survival link chain of OHCA, and it is imperative to recognize symptoms and signs of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) to ensure timely intervention.4
References-
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/01.CIR.0000147236.85306.15
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0019483223001402?via%3Dihub
- https://doi.org/10.1111/nicc.12631
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ihj.2023.08.005
Learn how the Codex Mechanical CPR Device can save lives!
Book a demo today or contact us on +91-7385304200 for more details on how this innovative technology can enhance the emergency response and improve survival rates.